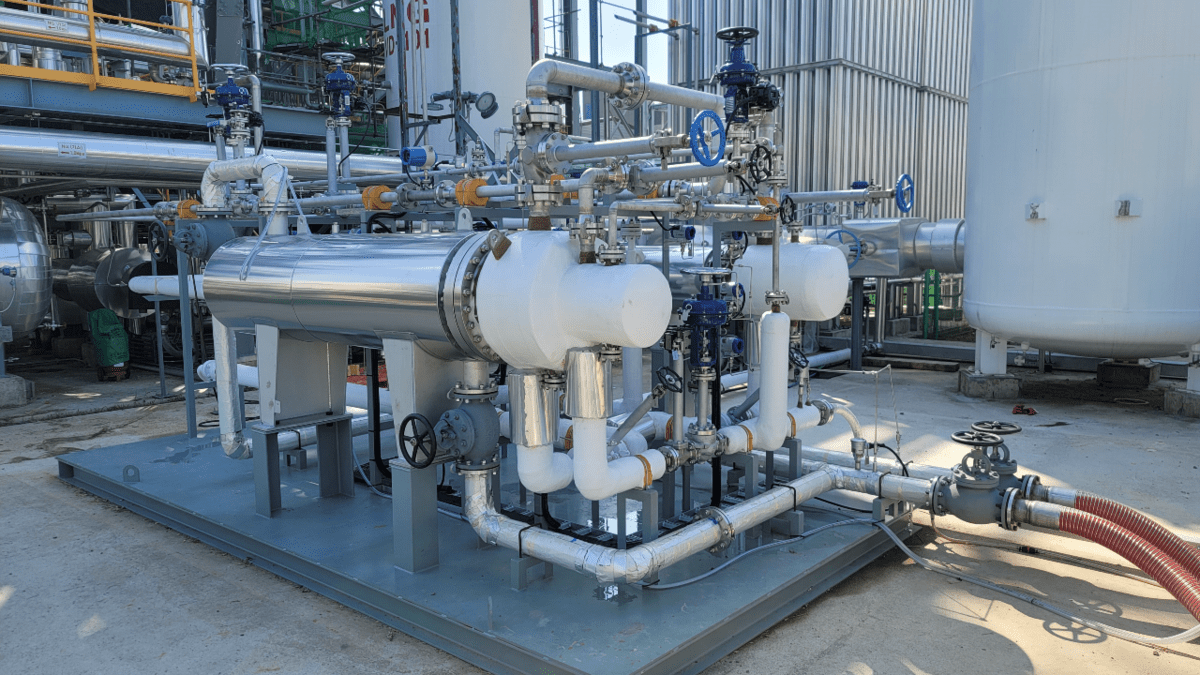
With LNG-fuelled ships being ordered in record numbers, Korea Shipbuilding & Offshore Engineering (KSOE) and its subsidiary Hyundai Heavy Industries (HHI) have developed a new waste heat-derived LNG fuel supply system that will cut fuel consumption and reduce emissions
Designed for 300,000-dwt very large crude carriers, the new Hi-eGAS system (Hyundai high-efficient gas supply system) has received an approval in principle (AiP) from DNV. The system uses waste heat from engine cooling water as a heat source for LNG-fuelled ships. This has been trialled previously, but commercialisation was not successful due to concerns that engine performance could be negatively affected.
Hi-eGAS consists of a safety system in which the engine will continue running normally in the event of an incident to the LNG fuel system, such as forcing vaporiser leakage or failure of the JCW booster pump, temp and pressure control valves.
The system utilises a new heat exchanger with low freezing risk, which KSOE and HHI developed in co-operation with domestic equipment companies. Currently, LNG fuel propulsion ships have used boilers to make hot steam, which has converted LNG into a gas at room temperature to supply a ship’s engine. However, this process has the disadvantage of increasing fuel costs and carbon emissions.
KSOE successfully completed a 24-hour demonstration test last year at the LNG Cryogenic Mechanical Testing Certification Center at the Korea Institute of Machinery and Materials under the same conditions as the maximum fuel supply for large ships.
“KSOE and HHI are leading the development of reducing carbon emissions and high-efficiency ship technology that increases the competitiveness of LNG fuel propulsion ships,” said KSOE vice president Byeongyong Yoo. “I believe that AiP of this technology, proven by DNV, can provide more confidence in stakeholders’ choices and support shipping industries to lower fuel price and CO2 emissions.”
As IMO’s environmental regulations, especially on ships’ carbon emissions, are tightened, LNG is expected to become a primary fuel for ships. In total, 805 LNG-fuelled vessels are on order or in operation, with a further 229 LNG-ready vessels, according to DNV’s Alternative Fuels Insight platform. In 2022 alone, more than 150 vessels were ordered with LNG as ship fuel.
“DNV aims to support the transition of the shipping and shipbuilding industries to a cleaner, green future. Our role is to ensure the new technology will offer better solutions to the maritime industry in a continually evolving fuel landscape,” said DNV Maritime Korea and Japan regional manager Vidar Dolonen.