LPG distributer Astomos Energy Corporation, Sustainable Energy Development, and Nippon Yusen Kabushiki Kaisha (NYK) have agreed to jointly study converting organic waste generated on board to fuel.
Waste generated on board is typically stored on deck and discharged at port. It can be substantial. For example, approximately 5,000 litres of waste, mainly plastic dust, is generated from a large LPG carrier for every 45-day voyage between Japan and the Middle East.
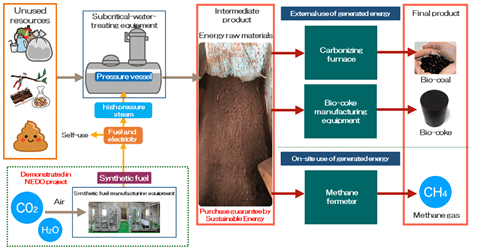
The companies plan to utilise this waste by installing Sustainable Energy’s ISOP system onboard ships to generate biofuel from combustible garbage and other materials.
ISOP can reduce CO2 emissions from the entire organic waste treatment process by converting the bio-components of the waste into fuel. ISOP does not require waste segregation.
With it, more space will be made available onboard and the sanitary conditions of seafarers will be improved, says NYK.
The three companies will proceed with a joint study targeting completion of the onboard demonstration test and implementation of ISOP on a vessel by the mid-2020s.